The debate between decentralization and centralization is central to understanding why blockchain technology has become such a game-changer. Centralized systems have dominated industries for decades, but decentralization is emerging as a compelling alternative, particularly with the rise of blockchain technology. While both approaches have their strengths and weaknesses, the key to understanding blockchain’s importance lies in the advantages of decentralization.
What is Centralization?
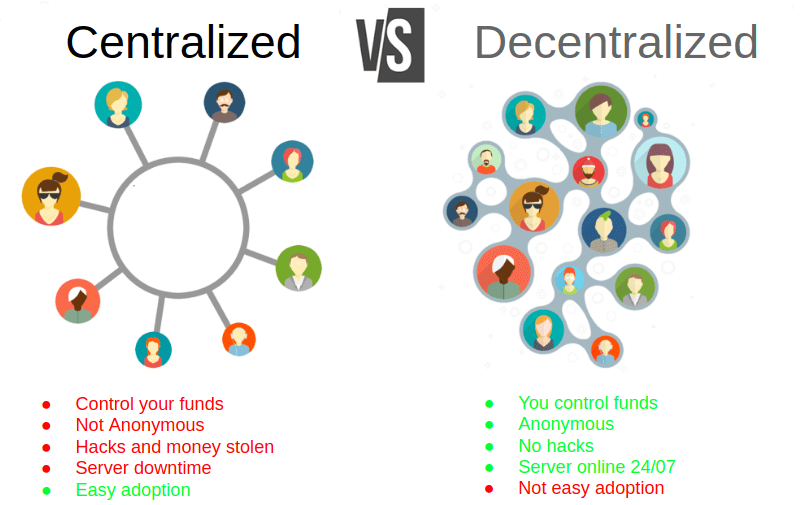
Centralization refers to a system in which control and decision-making are concentrated in the hands of a single entity or a small group. This is the model used by traditional banking systems, corporations, and governments. In a centralized system, all information flows through a central authority that is responsible for managing the system’s operations.
For example, in the financial industry, central banks control the monetary supply and policies, while commercial banks act as intermediaries between individuals and their money. Users must trust these institutions to manage their money securely and fairly. Similarly, in social media platforms like Facebook, a centralized company controls the platform and has access to all user data, making decisions about how the platform operates, what content is allowed, and how users interact with each other.
While centralization can lead to efficiency and streamlined decision-making, it also has its drawbacks. Centralized systems are vulnerable to attacks, corruption, and censorship. If the central authority fails or is compromised, the entire system can collapse. Additionally, users in centralized systems often have little control over their data or assets, as they must rely on the central authority to act in their best interests.
What is Decentralization?
Decentralization, in contrast, refers to a system in which control is distributed among many participants rather than being concentrated in a single entity. In a decentralized system, there is no central authority, and decisions are made collectively by the participants in the network. This approach is the foundation of blockchain technology.
In a decentralized blockchain, such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, transactions are verified by a network of nodes (computers) that work together to maintain the integrity of the ledger. No single entity controls the entire network, and changes to the system can only be made through a consensus of the participants. This creates a trustless system where users do not need to rely on intermediaries to verify transactions or manage their assets.
The Advantages of Decentralization
Decentralization offers several key advantages over centralized systems, which is why blockchain has become so important in the modern digital landscape.
Increased Security: Decentralized systems are inherently more secure because there is no single point of failure. In a centralized system, if the central authority is hacked, the entire system is compromised. In contrast, in a decentralized system, the network is distributed across many nodes, making it much harder for a hacker to take control. Even if one node is compromised, the rest of the network can continue to operate securely.
Greater Transparency: In decentralized systems, all transactions and changes to the ledger are recorded publicly and can be verified by anyone. This transparency reduces the risk of fraud and corruption, as all participants can see how the system is functioning. Blockchain’s immutability also ensures that once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered, providing a high level of accountability.
Elimination of Intermediaries: One of the most revolutionary aspects of blockchain is its ability to remove intermediaries. In traditional systems, intermediaries such as banks, notaries, or brokers are needed to verify transactions and manage assets. In a decentralized blockchain, users can transact directly with each other, without the need for third-party validation. This reduces costs and speeds up transactions, particularly in industries like finance and real estate.
Censorship Resistance: Decentralization makes it much harder for governments or corporations to censor or control information. In a centralized system, the authority can decide what information is allowed or restricted. However, in a decentralized system, no single entity has the power to control or censor the network. This is especially important in countries with restrictive regimes or in industries where freedom of information is crucial.
The Role of Blockchain in Decentralization
Blockchain is the technology that makes decentralization possible on a large scale. By providing a distributed ledger that is maintained by a network of nodes, blockchain enables secure, transparent, and tamper-proof transactions without the need for a central authority. This has significant implications for a wide range of industries, from finance to healthcare to supply chain management.
One of the most well-known examples of blockchain’s power is Bitcoin, a decentralized digital currency. Unlike traditional currencies that are controlled by central banks, Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network where users can send and receive payments directly without intermediaries. This has led to Bitcoin being seen as a hedge against centralized financial systems, particularly in times of economic uncertainty or instability.
Ethereum takes decentralization a step further by enabling the creation of decentralized applications (dApps) through smart contracts. These are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. Because they run on a decentralized blockchain, they cannot be altered or censored, providing a new level of trust and security for digital agreements.
Challenges of Decentralization
Despite its advantages, decentralization is not without its challenges. One of the primary issues is scalability. Decentralized systems, particularly those using Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanisms, can be slower and less efficient than centralized systems, especially when handling large numbers of transactions. This has led to the development of alternative consensus mechanisms like Proof of Stake (PoS) and layer-2 solutions to improve scalability.
Another challenge is governance. In a decentralized system, decision-making is shared among all participants, which can lead to disagreements and slow down the process of implementing changes. While this collective decision-making is a key feature of decentralization, it can also be a drawback when quick decisions are needed.
Conclusion
The debate between decentralization and centralization will likely continue as blockchain technology evolves. While centralized systems offer efficiency and control, decentralization provides greater security, transparency, and freedom. Blockchain has proven that decentralized systems can work at scale, offering a viable alternative to traditional centralized models. As blockchain continues to develop, the advantages of decentralization will likely become more apparent, driving further innovation in industries across the globe.






