Blockchain is a revolutionary technology that has transformed industries, particularly in the financial sector. At its core, blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger that records transactions across multiple computers. It ensures the security, transparency, and immutability of digital transactions. Unlike traditional databases that are controlled by a single entity, blockchain relies on a peer-to-peer network of nodes (computers), making it decentralized and less vulnerable to attacks or corruption.
How Does Blockchain Work?
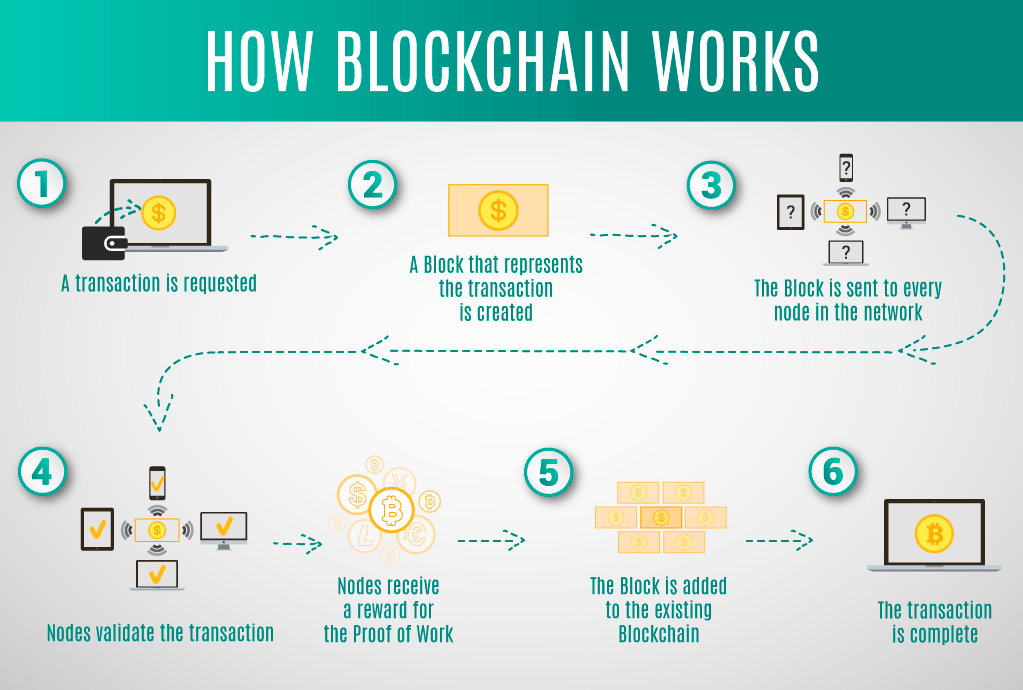
The structure of blockchain revolves around blocks. Each block contains a group of transactions, and once the block is filled, it is added to the chain. The blockchain grows over time as more blocks are added, forming a secure, chronological sequence of data. Each block is cryptographically linked to the previous one through a “hash,” a unique code that acts as the block’s fingerprint. If someone tries to alter a block’s content, the hash changes, disrupting the entire chain. This makes tampering nearly impossible without the majority’s approval.
Each transaction on a blockchain must be verified by the network through a consensus mechanism. The two most common mechanisms are Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). PoW, used by Bitcoin, requires participants (miners) to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and create new blocks. PoS, used by newer blockchains like Ethereum 2.0, assigns validation power based on the number of coins a participant holds, which consumes less energy than PoW.
Why Blockchain is Secure
Blockchain’s decentralized nature makes it highly secure. Since the data is distributed across many nodes, there is no single point of failure. Even if one node is compromised, the others maintain the integrity of the chain. Moreover, blockchain transactions are immutable—once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered. This immutability, combined with transparency, ensures trust without the need for intermediaries like banks or notaries.
Applications of Blockchain
While blockchain is widely known as the technology behind cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, its use cases extend far beyond digital currencies. Blockchain has the potential to revolutionize industries like healthcare, real estate, and supply chain management. For instance, in supply chains, blockchain can track the journey of a product from manufacturer to consumer, ensuring transparency and reducing the risk of fraud or counterfeiting. In healthcare, blockchain can securely store patient records, allowing authorized parties to access them while maintaining privacy and data integrity.
Governments are also exploring blockchain for secure voting systems. Traditional voting systems are vulnerable to fraud and hacking, but a blockchain-based system ensures that votes are accurately recorded and cannot be tampered with. This could increase trust in electoral processes and encourage voter participation.
Challenges and Future of Blockchain
Despite its many advantages, blockchain technology still faces challenges. Scalability is a significant issue, particularly for older blockchains like Bitcoin, which can only process a limited number of transactions per second. As blockchain adoption grows, finding solutions to scale the technology without compromising security is crucial.
Another challenge is energy consumption. PoW blockchains, especially Bitcoin, require vast amounts of computational power, leading to concerns about their environmental impact. Alternatives like PoS are gaining traction because they consume less energy while maintaining security.
In the future, blockchain technology is expected to evolve and become more integrated into everyday applications. Innovations like layer-2 solutions and sharding aim to improve scalability, while the development of decentralized applications (dApps) is opening new possibilities for businesses and individuals alike. Blockchain has the potential to reshape industries by fostering a more transparent, secure, and decentralized future.
Conclusion
Blockchain is more than just the backbone of cryptocurrencies; it’s a technology that promises to revolutionize many sectors. By providing a secure, decentralized, and transparent way to record transactions, blockchain can enhance trust and efficiency in systems that traditionally rely on intermediaries. As the technology matures and overcomes its current challenges, we are likely to see even more innovative uses of blockchain in the future.







